This version of the form is not currently in use and is provided for reference only. Download this version of
Form 5013-SB Schedule B
for the current year.
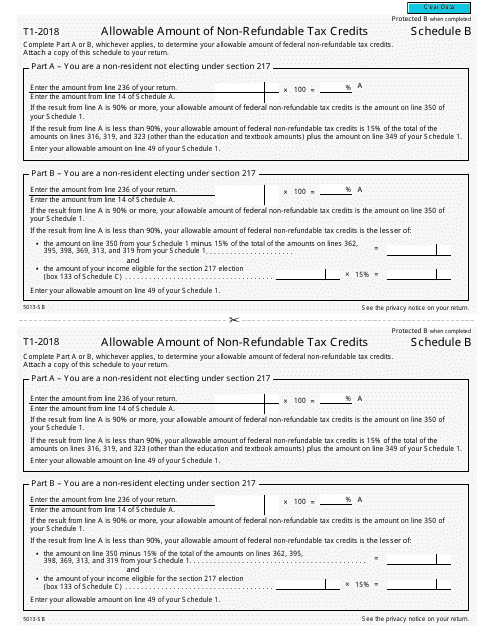
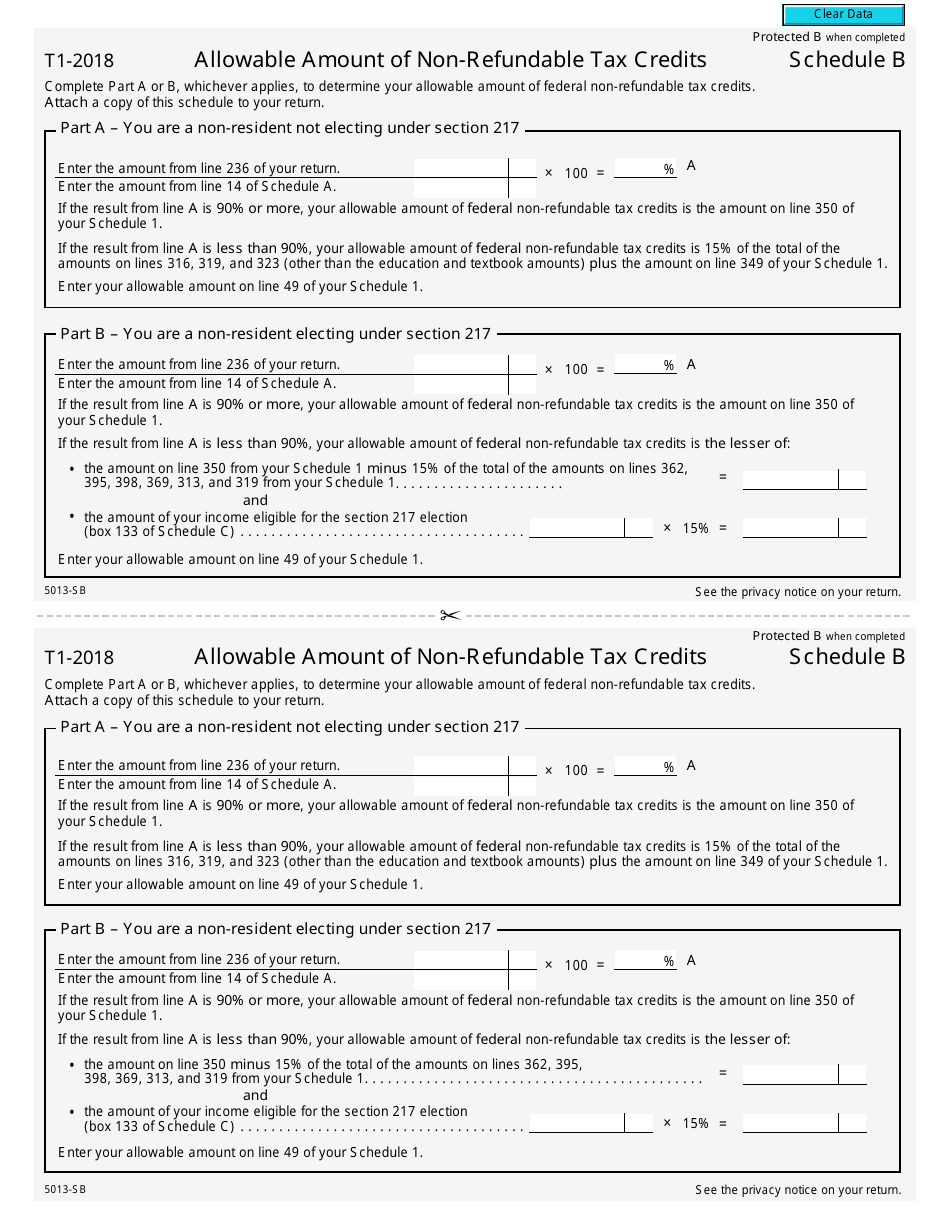
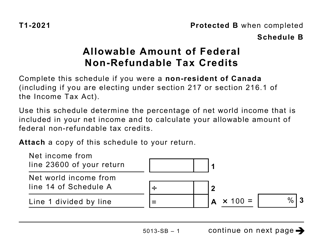
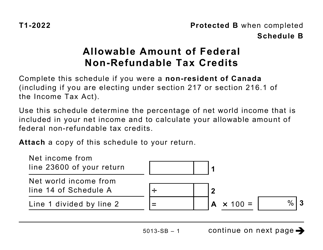
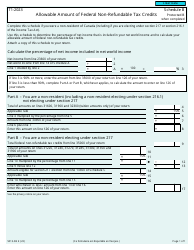
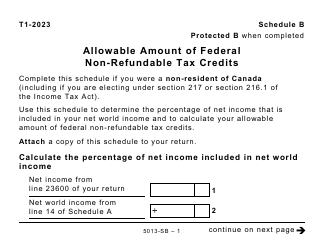
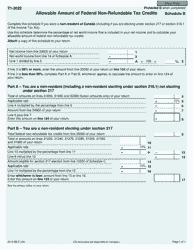
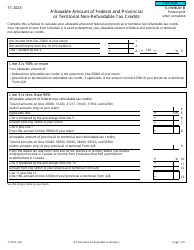
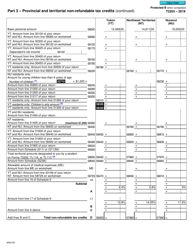
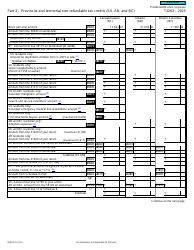
Form 5013-SB Schedule B Allowable Amount of Non-refundable Tax Credits - Canada
This Canada-specific " Allowable Amount Of Non-refundable Tax Credits " is a document released by the Canadian Revenue Agency .
Download the fillable PDF by clicking the link below and use it according to the applicable legal guidelines.
FAQ
Q: What is Form 5013-SB Schedule B?
A: Form 5013-SB Schedule B is a tax form used in Canada to calculate the allowable amount of non-refundable tax credits.
Q: What are non-refundable tax credits?
A: Non-refundable tax credits are deductions from your tax owed that can reduce the amount of tax you have to pay, but cannot result in a tax refund.
Q: What is the purpose of Form 5013-SB Schedule B?
A: The purpose of Form 5013-SB Schedule B is to determine the total amount of non-refundable tax credits that can be applied to your tax liability.
Q: How do I fill out Form 5013-SB Schedule B?
A: To fill out Form 5013-SB Schedule B, you need to enter the relevant information for each non-refundable tax credit you are eligible for, such as the amount of the credit and any supporting documentation required.
Q: Can non-refundable tax credits reduce my tax liability to zero?
A: Yes, non-refundable tax credits can reduce your tax liability to zero, but any excess credits cannot be refunded to you.
Q: What are some examples of non-refundable tax credits in Canada?
A: Some examples of non-refundable tax credits in Canada include the basic personal amount, the tuition and education amounts, and the medical expense credit.
Q: Can non-refundable tax credits be carried forward to future years?
A: Yes, if you are unable to fully utilize your non-refundable tax credits in the current year, you can carry them forward and apply them to your tax liability in future years.
Q: How do I know if I am eligible for non-refundable tax credits?
A: Eligibility for non-refundable tax credits depends on various criteria, such as your income level, expenses incurred, and specific circumstances. It is best to consult with a tax professional or refer to the Canada Revenue Agency (CRA) guidelines for specific eligibility requirements.