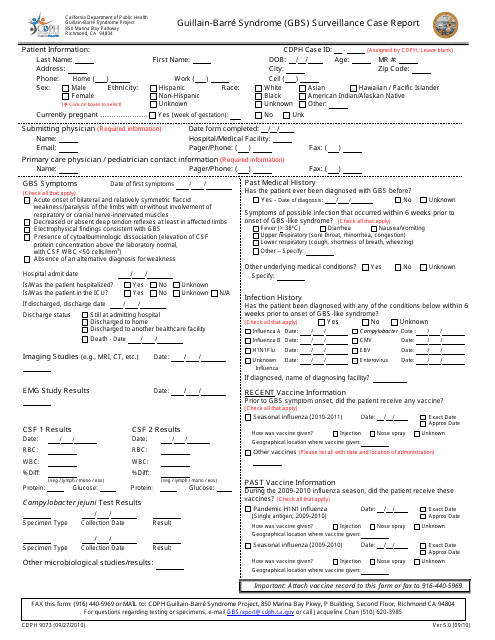
Form CDPH9073 Guillain-Barre Syndrome (Gbs) Surveillance Case Report - California
What Is Form CDPH9073?
This is a legal form that was released by the California Department of Public Health - a government authority operating within California. As of today, no separate filing guidelines for the form are provided by the issuing department.
FAQ
Q: What is Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS)?
A: Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS) is a rare neurological disorder where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the peripheral nerves.
Q: What are the symptoms of Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS)?
A: Symptoms of GBS include muscle weakness or paralysis, loss of reflexes, and tingling or numbness in the limbs.
Q: How is Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS) diagnosed?
A: GBS is diagnosed through a combination of medical history, physical examination, and tests such as nerve conduction studies and lumbar puncture.
Q: What causes Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS)?
A: The exact cause of GBS is unknown, but it is often preceded by an infection such as a respiratory or gastrointestinal infection.
Q: Is Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS) contagious?
A: No, GBS is not contagious. It is not spread from person to person.
Q: Is there a treatment for Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS)?
A: There is no cure for GBS, but treatment options include intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) therapy and plasmapheresis to help reduce symptoms and speed up recovery.
Q: Can Guillain-Barre Syndrome (GBS) be prevented?
A: There is no known way to prevent GBS, but practicing good hygiene and getting vaccinated against some infections may help reduce the risk.
Q: What is the surveillance case report for GBS in California?
A: The surveillance case report (Form CDPH9073) is a document used to track and monitor cases of Guillain-Barre Syndrome in California.
Form Details:
- Released on September 27, 2010;
- The latest edition provided by the California Department of Public Health;
- Easy to use and ready to print;
- Quick to customize;
- Compatible with most PDF-viewing applications;
- Fill out the form in our online filing application.
Download a printable version of Form CDPH9073 by clicking the link below or browse more documents and templates provided by the California Department of Public Health.