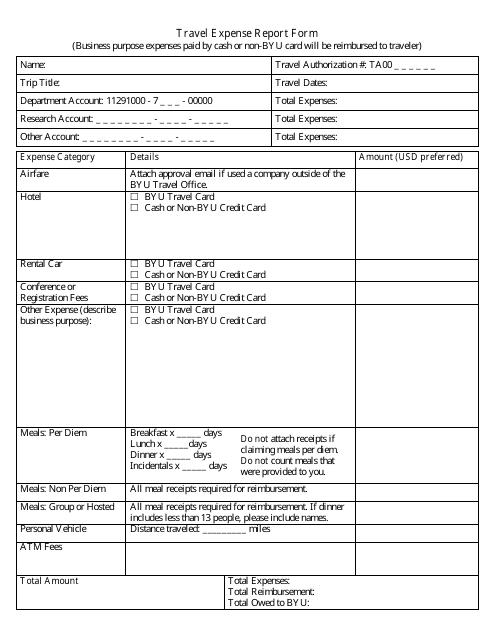
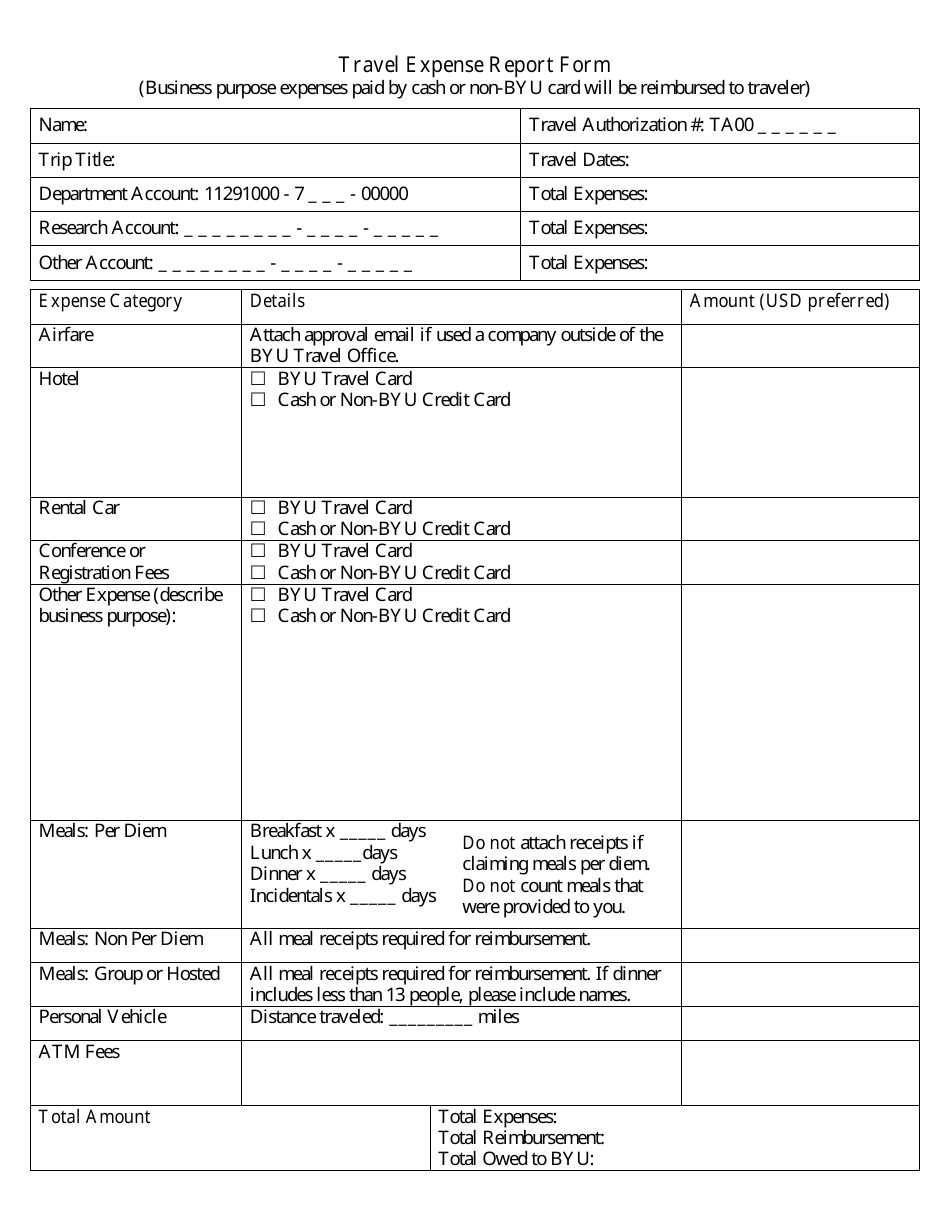
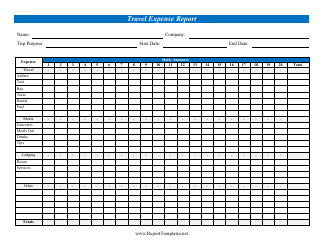
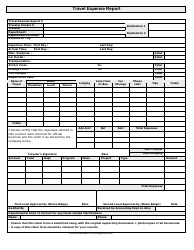
Travel Expense Report Form
The Travel Expense Report form is used to document expenses incurred during business travel. It helps employees report and request reimbursement for expenses such as transportation, accommodation, meals, and other related costs.
The person who incurs travel expenses typically files the Travel Expense Report Form.
FAQ
Q: What is a travel expense report form?
A: A travel expense report form is a document used to record and submit expenses incurred during business travel.
Q: Why is a travel expense report form necessary?
A: A travel expense report form is necessary to accurately track and account for expenses related to business travel.
Q: What information is typically included in a travel expense report form?
A: A travel expense report form usually includes details such as travel dates, destinations, purpose of the trip, transportation expenses, accommodation expenses, meals and entertainment expenses.
Q: Who needs to fill out a travel expense report form?
A: Employees or individuals who have incurred expenses during business travel are responsible for filling out a travel expense report form.
Q: Is a travel expense report form required for reimbursement?
A: Yes, a travel expense report form is typically required by companies or organizations for reimbursement of travel expenses.
Q: Can I use digital or electronic travel expense report forms?
A: Yes, many companies and organizations accept digital or electronic travel expense report forms. It is best to check with your employer or the company's policy regarding the use of digital forms.
Q: What should I do if I have lost receipts for my travel expenses?
A: If you have lost receipts for your travel expenses, you should still include the expenses in your travel expense report form. However, be prepared to provide an explanation and use other supporting documentation if available.
Q: How long should I keep a copy of my travel expense report form?
A: It is generally recommended to keep a copy of your travel expense report form and any related receipts or documentation for at least three to seven years, depending on your specific circumstances and the requirements of your employer or tax authorities.