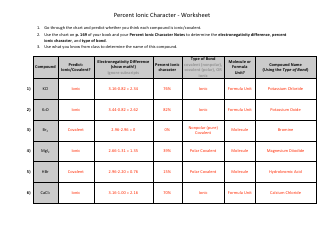
Chemistry Alkanes' Combustion Worksheet - United Kingdom
FAQ
Q: What is combustion?
A: Combustion is a chemical reaction in which a substance reacts rapidly with oxygen, releasing heat and producing light.
Q: What are alkanes?
A: Alkanes are hydrocarbons, which means they are made up of hydrogen and carbon atoms only. They contain single covalent bonds between carbon atoms.
Q: What is the general formula for alkanes?
A: The general formula for alkanes is CnH2n+2, where 'n' represents the number of carbon atoms in the molecule.
Q: What are some examples of alkanes?
A: Some examples of alkanes include methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8), butane (C4H10), and pentane (C5H12).
Q: How do alkanes undergo combustion?
A: Alkanes undergo combustion by reacting with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water vapor. This reaction releases energy in the form of heat and light.
Q: What are the products of the complete combustion of alkanes?
A: The products of the complete combustion of alkanes are carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapor (H2O).
Q: What are the products of the incomplete combustion of alkanes?
A: The products of the incomplete combustion of alkanes can include carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor (H2O), and soot (carbon particles).
Q: What is the purpose of balancing chemical equations?
A: Balancing chemical equations is necessary to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation. It obeys the law of conservation of mass.
Q: How to balance a chemical equation?
A: To balance a chemical equation, you can start by adjusting the coefficients in front of the reactants and products until the number of atoms of each element is equal on both sides.
Q: Why is it important to study combustion reactions of alkanes?
A: Studying combustion reactions of alkanes is important because it helps us understand how these fuels burn, the products formed, and the energy released. It has important implications for energy production and environmental impact.