Electrical Conductivity of Aqueous Solutions
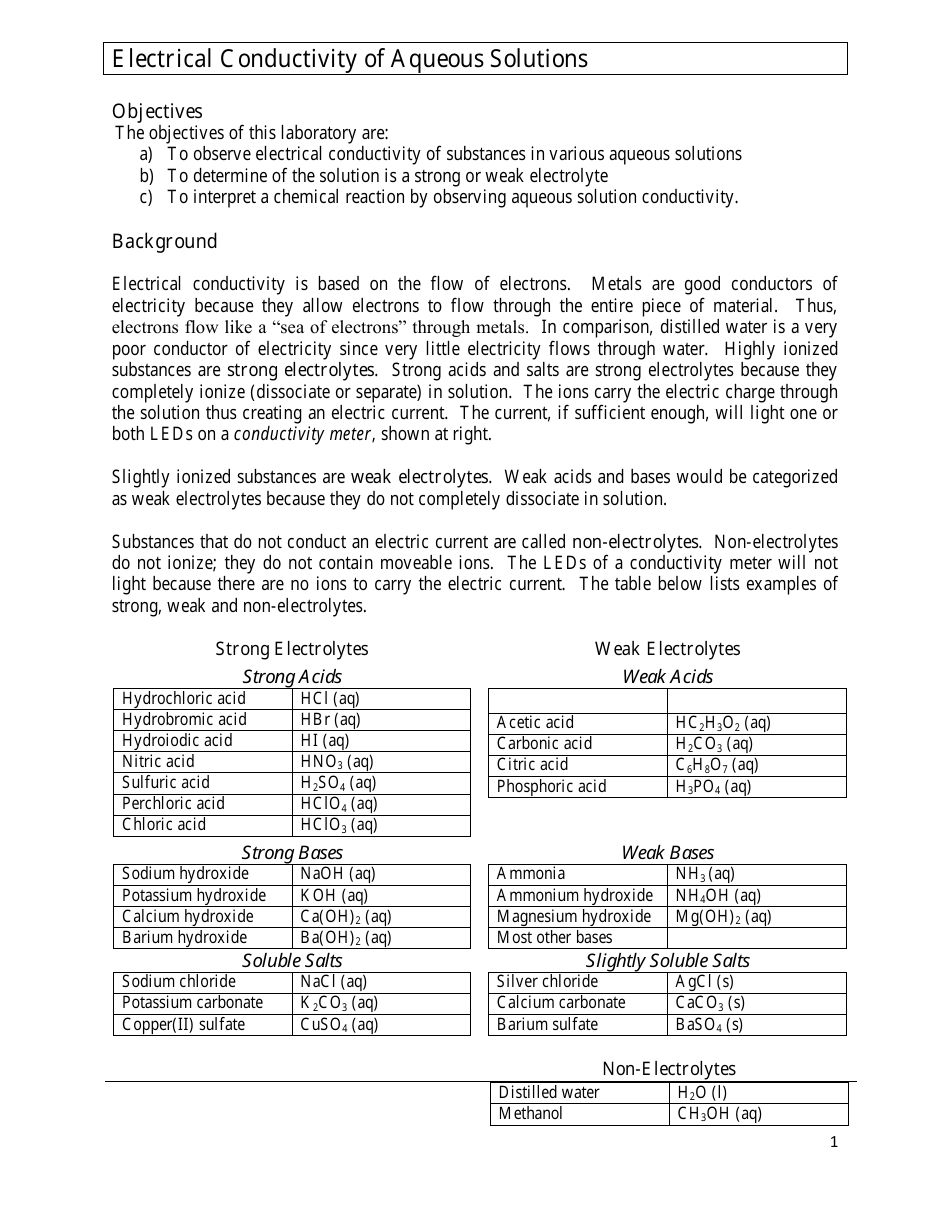
The electrical conductivity of aqueous solutions is used to determine the amount of dissolved ions or electrolytes in the solution. It helps in studying the properties of solutions, analyzing their composition, and understanding their behavior in various applications.
The electrical conductivity of aqueous solutions is typically filed by scientific researchers and academic institutions conducting experiments and studies in the field of chemistry and material science. Various research papers and scientific journals may contain information on the electrical conductivity of aqueous solutions.
FAQ
Q: What is electrical conductivity?
A: Electrical conductivity is the ability of a material to conduct electric current.
Q: What is an aqueous solution?
A: An aqueous solution is a solution in which water is the solvent.
Q: How does electrical conductivity of aqueous solutions work?
A: In aqueous solutions, electrical conductivity is a result of the movement of ions, or charged particles, in the water.
Q: What factors affect the electrical conductivity of aqueous solutions?
A: The concentration of ions, the type of ions present, and temperature can affect the electrical conductivity of aqueous solutions.
Q: What are some examples of substances that can create aqueous solutions with high electrical conductivity?
A: Strong electrolytes, such as salts and acids, can create aqueous solutions with high electrical conductivity.
Q: What are some examples of substances that can create aqueous solutions with low electrical conductivity?
A: Non-electrolytes, such as sugars and alcohols, can create aqueous solutions with low electrical conductivity.