Chemistry 12 - Predicting Precipitate Formation Worksheet
The Chemistry 12 - Predicting Precipitate Formation Worksheet is a learning resource primarily designed for high school students studying chemistry. It helps students practice the skill of predicting and identifying the formation of precipitates during chemical reactions. This worksheet is intended to enhance students' understanding of chemical reactions and their ability to apply principles of solubility to predict the formation and properties of precipitates. It may be used as a homework assignment, in-class activity, or as a study tool to reinforce classroom lessons on this specific topic in chemistry.
The Chemistry 12 - Predicting Precipitate Formation Worksheet is typically filed by the student who completed the worksheet. It is usually submitted to the teacher or professor for grading purposes.
FAQ
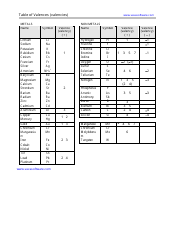
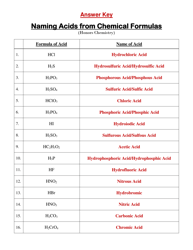
Q: What is a precipitate?
A: A precipitate is a solid that forms when two aqueous solutions react together.
Q: How can you predict if a precipitate will form?
A: To predict if a precipitate will form, you need to identify the reactants and products of the reaction and determine if the product is insoluble in water. If it is, a precipitate will form.
Q: What is solubility?
A: Solubility is the maximum amount of a solute that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a specific temperature.
Q: What are some common factors that affect solubility?
A: Temperature, pressure, and the nature of the solute and solvent are common factors that affect solubility.
Q: What is the solubility product constant (Ksp)?
A: The solubility product constant (Ksp) is an equilibrium constant that describes the degree of dissolution of an ionic compound in a saturated solution.
Q: How can you use the solubility product constant to predict precipitate formation?
A: If the ion product (IP) is greater than the solubility product constant (Ksp), a precipitate will form.
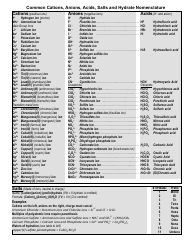
Q: What is a net ionic equation?
A: A net ionic equation shows only the species that participate in a chemical reaction and omits the spectator ions.
Q: Why are spectator ions omitted in a net ionic equation?
A: Spectator ions do not participate in the reaction and do not undergo any chemical change.
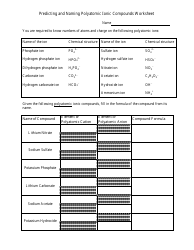
Q: What is a double displacement reaction?
A: A double displacement reaction is a chemical reaction in which two ionic compounds exchange ions to form two new compounds.
Q: What is a stoichiometric ratio?
A: A stoichiometric ratio is the balanced ratio of reactants and products in a chemical reaction.