Predicting and Naming Polyatomic Ionic Compounds Worksheet
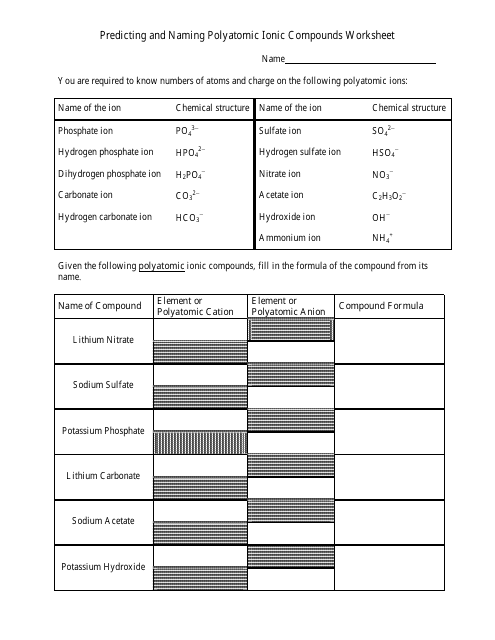
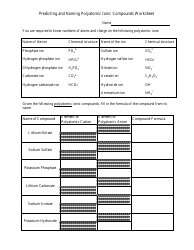
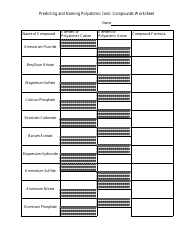
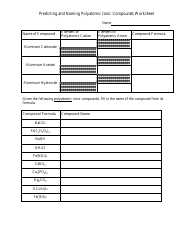
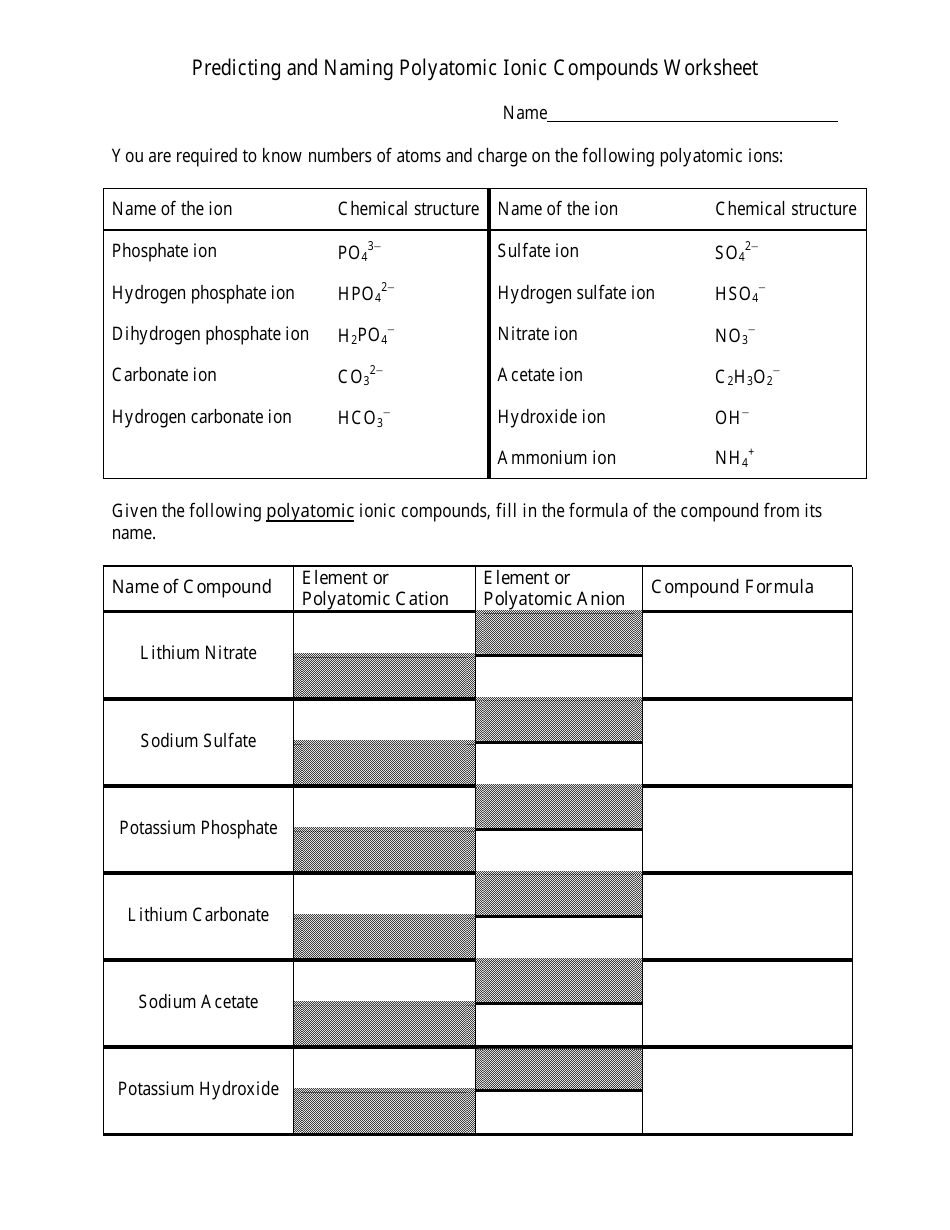
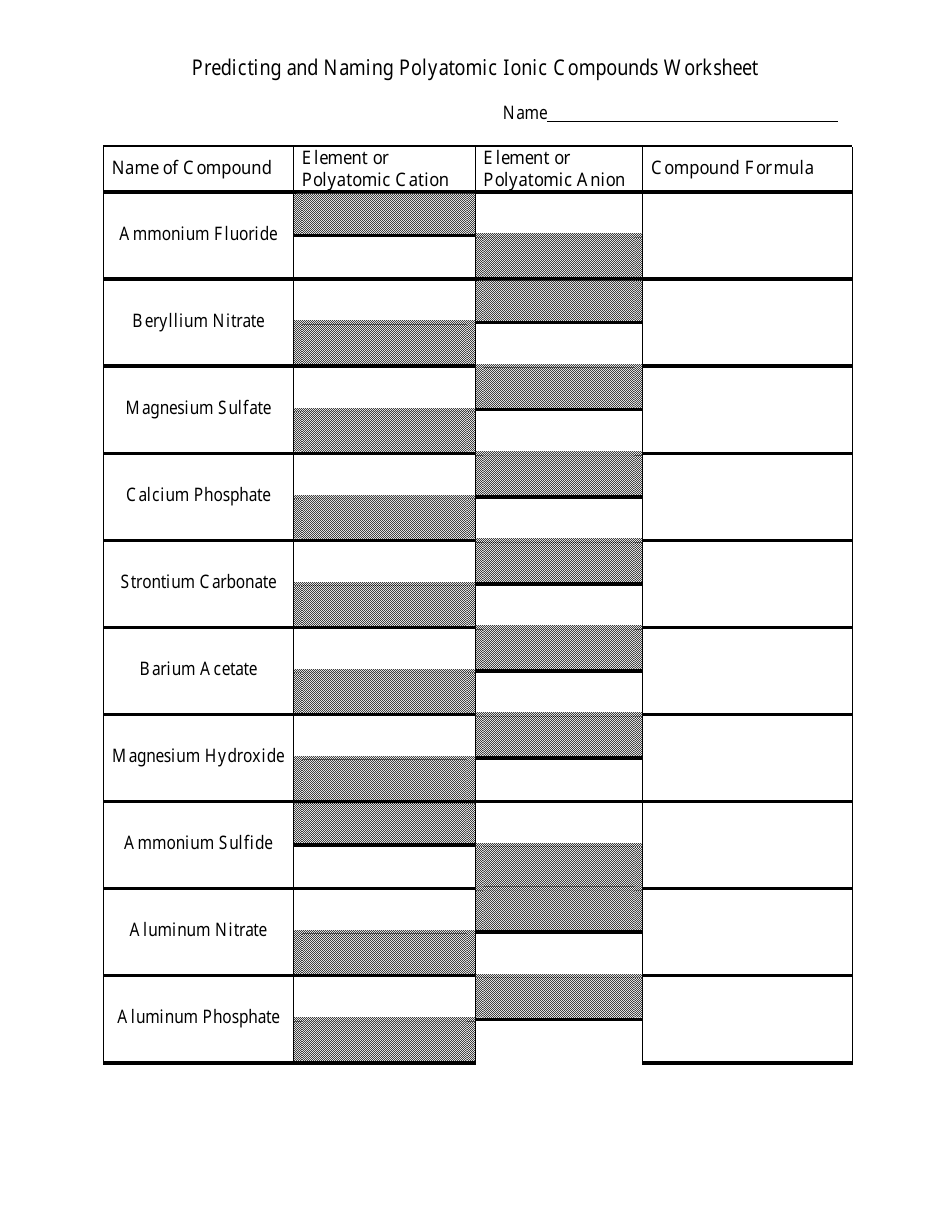
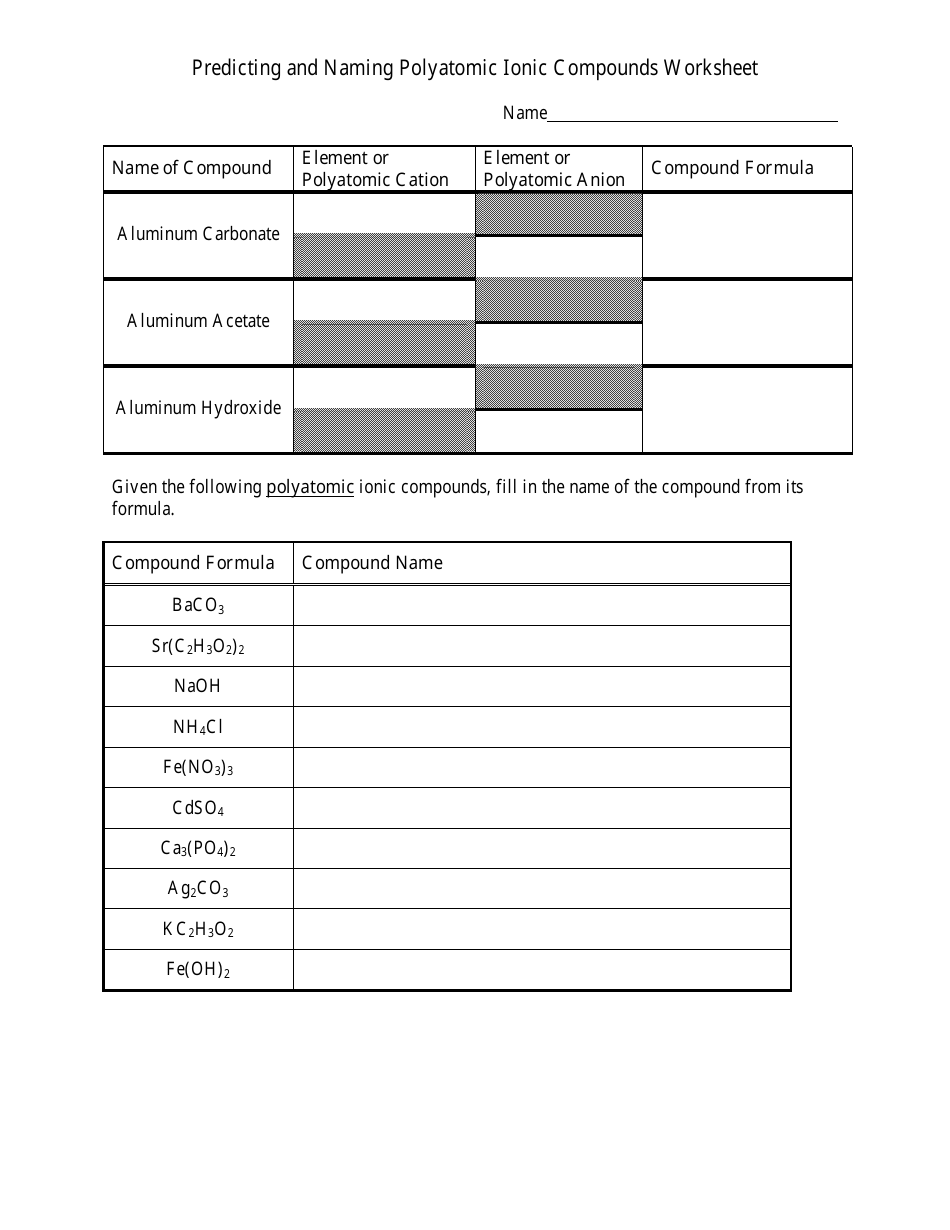
The worksheet "Predicting and Naming Polyatomic Ionic Compounds" is typically used as a learning tool in chemistry education. It is designed to help students practice predicting and naming polyatomic ionic compounds, which are compounds that contain positively and negatively charged polyatomic ions.
FAQ
Q: What are polyatomic ions?
A: Polyatomic ions are groups of atoms that carry a charge and act as a single unit in chemical reactions.
Q: How are polyatomic ions named?
A: Polyatomic ions are named based on a combination of the elements they contain.
Q: What are some examples of polyatomic ions?
A: Examples of polyatomic ions include sulfate (SO4^2-), nitrate (NO3^-), and ammonium (NH4^+).
Q: How do you predict the formula for a polyatomic ionic compound?
A: To predict the formula, you need to determine the charges of the ions and balance them to achieve a neutral compound.
Q: How are polyatomic ionic compounds named?
A: Polyatomic ionic compounds are named by listing the cation first, followed by the anion.
Q: What are some examples of polyatomic ionic compounds?
A: Examples of polyatomic ionic compounds include calcium carbonate (CaCO3), sodium sulfate (Na2SO4), and potassium hydroxide (KOH).