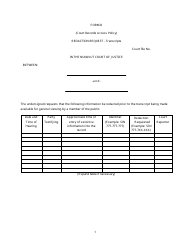
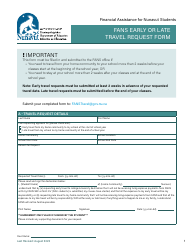
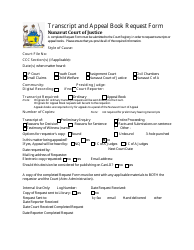
Request for Technology - Nunavut, Canada
The Request for Technology (RFT) in Nunavut, Canada is a process used to solicit technological solutions for specific needs or challenges in the region. It is aimed at acquiring technology that can improve various aspects of life in Nunavut, such as infrastructure, communication, or healthcare.
The request for technology in Nunavut, Canada is typically filed by the relevant government department or agency responsible for technology acquisition and implementation.
Request for Technology - Nunavut, Canada - Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What technology is used in Nunavut, Canada?
A: Nunavut utilizes various technologies, including telecommunications, internet services, transportation infrastructure, and renewable energy systems.
Q: How is internet connectivity in Nunavut?
A: Internet connectivity in Nunavut is primarily provided through satellite technology, which ensures coverage across the vast and remote territory.
Q: What transportation technologies are available in Nunavut?
A: Nunavut relies on transportation technologies such as airplanes, helicopters, ships, and snowmobiles to connect communities and facilitate movement within the territory.
Q: Are there renewable energy systems in Nunavut?
A: Yes, Nunavut has been investing in renewable energy systems, such as solar panels, wind turbines, and small-scale hydroelectric projects, to reduce reliance on diesel generators and promote sustainable energy sources.
Q: What technologies are used for communication in Nunavut?
A: Telecommunication technologies like satellite phones, internet services, and mobile networks are used for communication in Nunavut, bridging the distance between communities.
Q: How is technology improving life in Nunavut?
A: Technology plays a crucial role in improving life in Nunavut by enhancing communication, providing access to information, supporting healthcare services, and increasing economic opportunities.
Q: Are there any specific technological challenges faced in Nunavut?
A: Nunavut faces unique technological challenges due to its remote and vast geographical location, including limited internet bandwidth, high costs of infrastructure maintenance, and harsh weather conditions affecting connectivity.