Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Testing Request Form - Utah
Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Testing Request Form is a legal document that was released by the Utah Department of Health and Human Services - a government authority operating within Utah.
FAQ
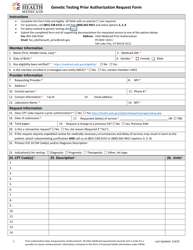
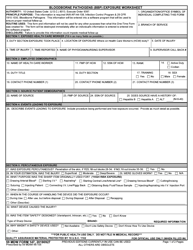
Q: What is a Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Testing Request Form?A: The Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Testing Request Form is a document used in Utah to request testing after potential exposure to bloodborne pathogens.
Q: What is a bloodborne pathogen?A: A bloodborne pathogen is a microorganism that can cause disease and is present in human blood or other body fluids.
Q: Why would someone need to fill out this form?A: Someone would need to fill out this form if they have potentially been exposed to bloodborne pathogens.
Q: How can someone get exposed to bloodborne pathogens?A: Exposure to bloodborne pathogens can occur through contact with infected blood or other body fluids, such as through needlestick injuries or contaminated items.
Q: What information is required on the form?A: The form typically requires personal information of the individual who was exposed, details about the exposure incident, and information about the source individual (if known).
Q: What should someone do if they think they have been exposed to bloodborne pathogens?A: If someone believes they have been exposed to bloodborne pathogens, they should seek medical attention immediately and follow the recommended steps for reporting the incident and requesting testing.
Q: Is there a cost associated with getting tested for bloodborne pathogens?A: Costs for testing may vary depending on the healthcare facility or provider, and some individuals may have coverage through insurance or workplace policies.
Q: What are some common bloodborne pathogens?A: Common bloodborne pathogens include HIV, hepatitis B, and hepatitis C.
Q: Can bloodborne pathogens be transmitted through casual contact?A: No, bloodborne pathogens are not typically transmitted through casual contact, but rather through direct blood-to-blood contact or contact with other potentially contaminated body fluids.