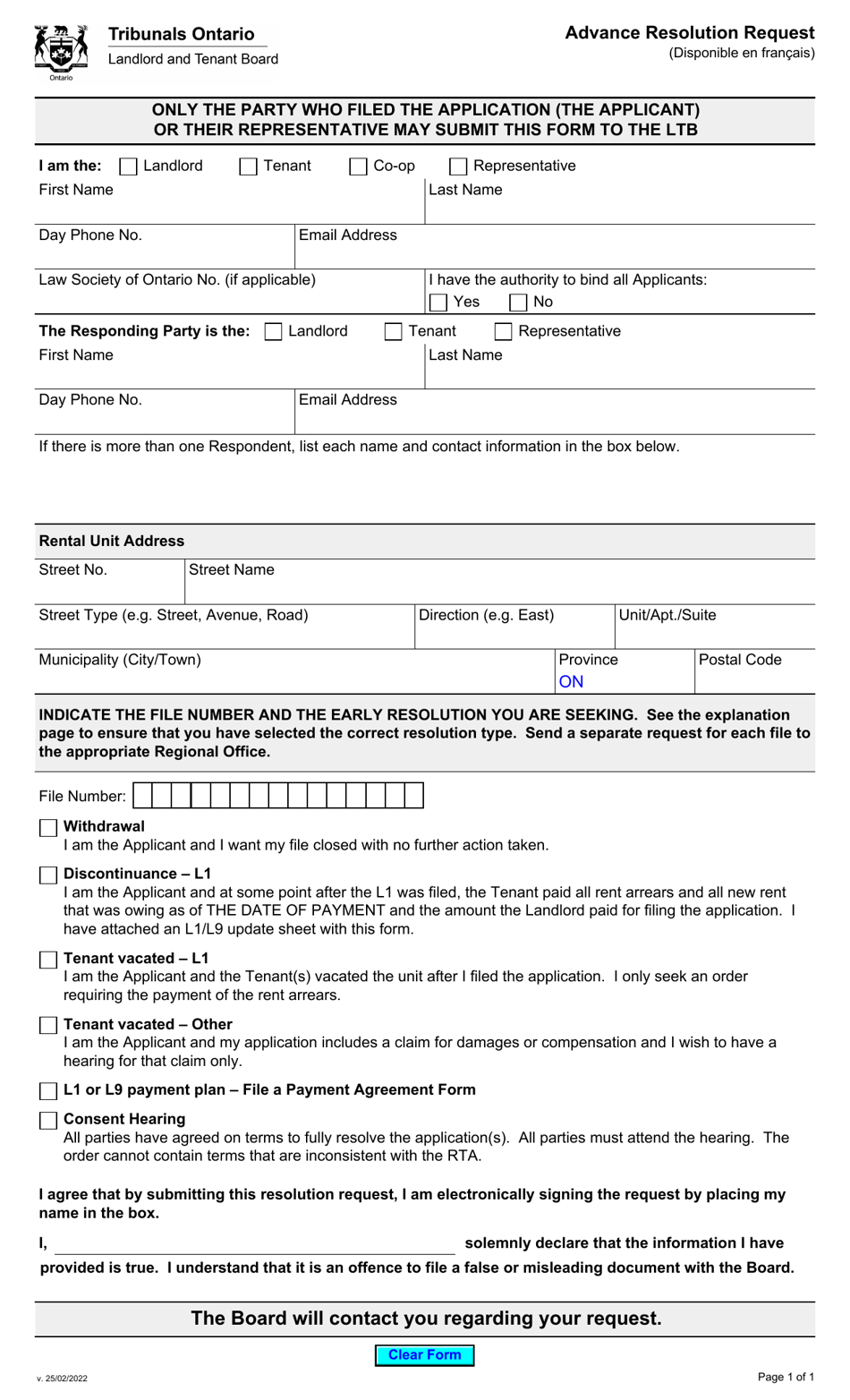
Advance Resolution Request - Ontario, Canada
An Advance Resolution Request in Ontario, Canada is a process to address issues or concerns related to services provided by the government. It allows individuals to seek a resolution before further escalation or legal action.
In Ontario, Canada, the Advance Resolution Request is filed by the person or organization named as the respondent on the document.
Advance Resolution Request - Ontario, Canada - Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What is an Advance Resolution Request?
A: An Advance Resolution Request is a formal process used in Ontario, Canada to resolve a dispute between individuals or organizations before it goes to court.
Q: Who can file an Advance Resolution Request?
A: Any individual or organization involved in a dispute in Ontario, Canada can file an Advance Resolution Request.
Q: What types of disputes can be resolved through an Advance Resolution Request?
A: A wide range of disputes can be resolved through an Advance Resolution Request, including issues related to contracts, property, employment, and other civil matters.
Q: How does the Advance Resolution Request process work?
A: The process involves submitting a written request to the appropriate authority, providing the necessary information and documents, and participating in a resolution meeting or mediation.
Q: Is the Advance Resolution Request process legally binding?
A: No, the process is voluntary and the outcome is not legally binding, unless agreed upon by all parties involved.
Q: Are there any fees involved in filing an Advance Resolution Request?
A: Yes, there are fees associated with filing an Advance Resolution Request, which vary depending on the nature and complexity of the dispute.
Q: What are the benefits of using the Advance Resolution Request process?
A: The process is generally faster, less formal, and less expensive than going to court. It also allows parties to have more control over the resolution of their dispute.
Q: Can I still go to court if the Advance Resolution Request process does not resolve my dispute?
A: Yes, if the dispute remains unresolved through the Advance Resolution Request process, you can still pursue legal action through the courts.