Ordinary Dividends Templates
Ordinary Dividends, also known as Dividend Income, are a type of income that individuals receive from owning stocks and other investments. These dividends are typically paid out by corporations as a way to distribute a portion of their profits to shareholders.
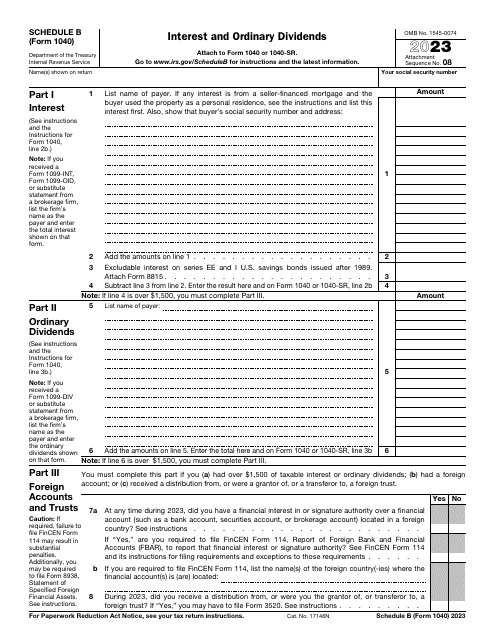
To accurately report and calculate your ordinary dividends, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) requires individuals to fill out specific forms and follow certain guidelines. One such form is the IRS Form 1040 Schedule B Interest and Ordinary Dividends. This form allows taxpayers to detail their interest and dividend income, including any ordinary dividends received.
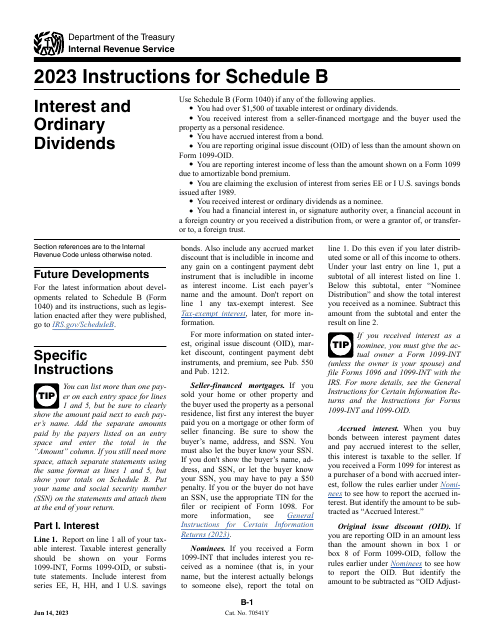
The Instructions for IRS Form 1040 Schedule B Interest and Ordinary Dividends provide step-by-step guidance on how to complete the form correctly. It covers important details such as which types of dividends are considered ordinary, how to report these dividends accurately, and any applicable deductions or credits related to dividend income.
Properly reporting your ordinary dividends is crucial to ensure that you meet your tax obligations and avoid any penalties or audits. By using the IRS Form 1040 Schedule B Interest and Ordinary Dividends and following the instructions provided, you can accurately report your dividend income and ensure compliance with tax regulations.
Whether you are a novice investor or a seasoned shareholder, understanding and appropriately reporting your ordinary dividends is essential. Familiarize yourself with the IRS Form 1040 Schedule B Interest and Ordinary Dividends and its accompanying instructions to ensure that you are correctly reporting your dividend income. By doing so, you can confidently fulfill your tax obligations while maximizing your financial well-being.
Documents:
9
This is a supplementary form individuals are supposed to use to calculate income tax they owe after receiving interest from bonds and earning dividends.